The word
helminth, worm, is commonly used in Parasitology. Two phylae of helminths are important in Parasitology:
flatworms, and
nematodes, roundworms (in old and alternative classifications appear in the Aschelminth phylum).
Platyhelminthes are flatworms, most are hermaphrodites and many are parasitic.
Clonorchis sinensis affects more than 30 million people worldwide, especially in Asia. It is caused by consuming fresh or semi-processed fish or shellfish. The genus
Opistorchis has a similar behavior, affecting, in addition to the human species, other mammals and fish.
Fasciola hepatica is a parasitic worm of the bile ducts and gallbladder of numerous species, including human. In livestock, it is one of the most widespread parasites in ruminants, especially cattle, goats and sheep, although it can also affect horses and lagomorphs. Its intermediate hosts are aquatic snails.
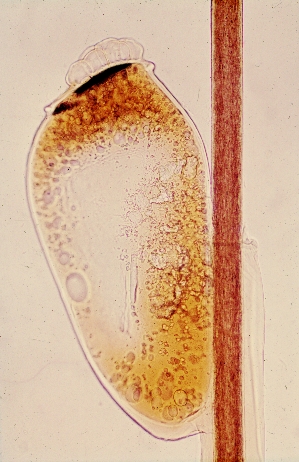
Schistosomiasis is produced by trematodes of the genus
Schistosoma. It is not usually a serious illness, although it is incapacitating, mainly by the fever. Its biological cycle is typical of the trematodes, alternating in the same species of vertebrates and invertebrates.
.svg/726px-Schistosoma_(ciclo_vital).svg.png) |
| Life cycle of Schistosoma |
Taenia solium is transmitted to humans through uncooked or undercooked pork enters the human species generally through pork, while
Taenia saginata does it for beef. Humans are generally infected for eating raw or undercooked beef which contains the infective larvae, called cysticerci.
The hydatid cyst is produced by
Echinococcus granulosus. It is hydatidosis, which occurs in human species and certain animals, such as the dog and the sheep. It is produced by ingesting food contaminated by feces that contain the parasite. The disease can become deadly, as cysts can affect the liver, lungs, bones, kidneys or brain.
 |
| Hydatid cyst in lamb's liver |
Nematodes form a large part of the planet's biomass and are critical to maintaining ecosystems. Parasite nematodes are a minority group of all nematodes.
Trichuriasis, also known as whipworm infection, is caused by the nematode
Trichuris trichiura, which is characterized by gastrointestinal problems and diarrhea.
Trichinosis is produced by nematodes of the genus
Trichinella through eating undercooked meat containing
Trichinella cysts, most often this is pork but can also occur from bear and dog meat. This causes muscle pain, fever and gastrointestinal disorders. When the parasite reaches the heart, the consequences can be lethal or cause heart problems. If the infestation is massive it can cause death by the traumatic effect of the invasion of the tissues. For this reason, pork should not be consumed, if not analyzed with the trichinoscope, a microscope adapted for this purpose.
 |
| Trichinella spiralis, in muscle tissue |
Strongyloides stercoralis produces strongyloidiasis. It is a common nematode in warm and humid areas. Strongyloidiasis is an important disease in immunocompromised persons and can cause a hyperinfection syndrome that can lead to death if untreated. It's produced by the contact of soils contaminated with feces.
Ancylostoma duodenale is a nematode that causes the hookworm infection, together with
Necator americanus. It's one of the most frequent parasitosis in the world, which is contracted by the skin or orally in places of poor hygiene.
Ascaris lumbricoides causes ascariasis, in which the multiplication of helminths in the intestine causes health problems, such as diarrhea, pallor, malnutrition, etc. They may cause visceral damage, peritonitis, inflammation, appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, or migrate to other organs. The genus
Toxocara affects several species, in addition to the human, such as canids and felids; In animals larvae migrate throughout the body and only affect the human species if the number of larvae is very high and the individual is immunosuppressed.
Anisakis are parasites of fish that can affect the human species; Have proliferated in recent times, perhaps because of bad fishing practices (such as throwing guts into the sea) or changes in weather conditions.
The pinworm, also known as threadworm in the United Kingdom and Australasia or seatworm, is the specie
Enterobius vermicularis, that causes pinworm infection, also known as enterobiasis, a disease spread all over the world, mainly affecting children under 12 years old, who spread the disease by scratching the anus by itching, extending the eggs of the parasite.
Filarias are parasitic nematodes that cause terror.
Wuchereria bancrofti and
Brugia malayi are transmitted through the mosquito bite, living in the lymphatic system and causing an enormous dilation of the tissues.
Loa loa is transmitted through the sting of horseflies, living in the subcutaneous tissue.
Onchocerca volvulus causes onchocerciasis, which is transmitted through the black fly, microfilariae move through the body and if they reach the eyes can cause blindness.
Dranunculus medinensis (in the photo below) affects the subcutaneous tissues and causes dracunculiasis, is transmitted by ingesting contaminated water.
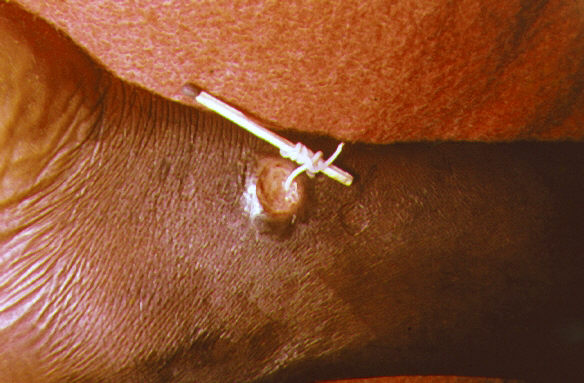 |
Dranunculus medinensis extracted through the skin
|
Acanthocephala is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, that possess a reversive proboscis with spines by which they adhere to the mucosa of the host.
Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus have veterinary importance as it affects the pig.
The
leeches are segmented worms that belong to the phylum Annelida and comprise the subclass Hirudinea. They live in the fresh water.
Hirudo medicinalis is the common leech, which feeds on blood, distributed throughout much of Europe in fresh water. However, pollution, habitat destruction and hunting have almost completely eliminated their presence in the wild landscape.
Pentastomida are a group of parasitic crustaceans commonly known as tongue worms. All are obligate parasites with correspondingly degenerate anatomy.
Linguatula serrata is a cosmopolitan zoonotic parasite, live in the nasopharyngeal region of mammals. Cats, dogs, foxes, and other carnivores are hosts of the parasite.
1. Platyhelminthes. General Characteristics and Classification
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Flatworm
- Video:
MicroStudent916. Helminths
- Video:
Hark 07. Phylum Platyhelminthes
2. Clonorchis, Opisthorchis and Paragonimus
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Clonorchis sinensis
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Opistorchis viverrini
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Opistorchis felineus
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Paragonimus
- Video:
TheLancetTV. Clonorchiasis
- Video:
Miguel Vicente. Paragonimus westermani
3. Fasciola. Other trematoda
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Fasciola hepática
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Trematoda
- Video:
MrChrisLeavitt. Sheep Liver Fluke Fasciola hepatica
4. Schistosoma
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Schistosoma
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Esquistosomiasis
- Video:
Xistose.com. Schistosoma mansoni casal (Schistosoma mansoni couple)
5. Cestoda. General Characteristics and Classification
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Cestoda
- Video:
History Of Mankind Documentary. Worms - Documentaries - History Documentary
6. Pseudophyllidea: Diphyllobothrium latum
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Diphyllobothrium
- Video:
NEJMvideo. Live Diphyllobothrium Latum during Colonoscopy
7. Ciclophyllidea: Taenia
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Taenia (genus)
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Taenia solium
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Taenia saginata
- Video:
African Veterinary Information. Taenia solium cysticercosis: Life cycle, epidemiology and diagnosis
8. Echinococcus. Other cyclophyllidea
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Echinococcus
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Echinococcus granulosus
- Video:
Neglected Tropical Diseases. Echinococcosis Documentry
9. Nematodes: General Characteristics and Classification
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Nematoda
- Video:
7activestudio. Nematoda General Characters
10. Trichuris trichiura. Other trichuridae
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Trichuris trichiura
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Trichuridae
- Video:
DrMurraSaca. Parasite in the Colon whipworm Trichuris trichiura
11. Trichinella
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Trichinella
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Trichinosis
- Video:
Everything For You. Trichinell Spiralis (Complete Overview )
12. Strongyloides stercoralis
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Stronglyoides stercoralis
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Strongyloidiasis
- Video:
Strongyloides stercoralis Larva life cycle
13. Uncinarias: Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus
- Lectura:
Wikipedia. Ancylostoma duodenale
- Lectura:
Wikipedia. Necator americanus
- Video:
Top Amazing. Parasite : Amazing found Ankylostome worm / Ancylostoma duodenal
- Video:
BirdWhisperer46. Nematode - Necator americanus - Hook Worm
14. Ascaris lumbricoides. Toxocara, Anisakis. Other ascarids
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Ascaris lumbricoides
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Toxocariasis
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Anisakis
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Ascaris summ
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Toxocara canis
- Video:
A/G Geeks. Ascaris The Human Parasite
- Video:
Sally Cantle. Toxocara Canis - The Dog Roundworm
- Video:
Cristina Martínez. Anisakis Life Cycle (PARASITE project)
15. Enterobius vermicularis
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Pinworm_(parasite)
- Video:
Dr. Anisa Pal. ENTEROBIUS VERMICULARIS (gravid female) laying eggs-live video
16. Filarias: Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia and Loa
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Wuchereria bancrofti
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Brugia malayi
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Loa loa
- Video:
Flexiguru. Elephantiasis/Filariasis
17. Onchocerca volvulus. Dracunculus medinensis. Other filarioidea
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Onchocerca volvulus
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Dracunculus medinensis
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Filariasis
- Video:
PublicResourceOrg. Filariasis
18. Acantocephala. Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Acantocephala
- Reading
Wikipedia. Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus
19. Annelids leeches. Hirudo medicinalis
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Hirudinea
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Hirudo medicinalis
- Video:
Dzikieswinie. Leech with cocoon - Hirudinea - Hirudo
20. Pentastómida. Linguatula serrata
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Pentastomida
- Reading:
Wikipedia. Linguatula serrata
- Video:
Tamás Csordás. Linguatula serrata
Identification of helminth parasites. Virtual Lab
Resources for further learning
- Video:
Boppolyscience. Platyhelminthes
Spanish version of this page
Parasitology

.jpg/800px-Ixodes_hexagonus_(aka).jpg)






.svg/726px-Schistosoma_(ciclo_vital).svg.png)